

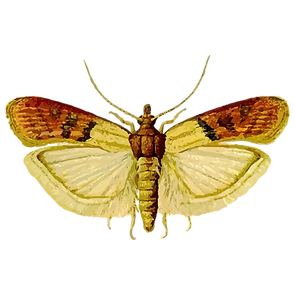
| Latin Name | Plodia interpunctella |
| Common Name | Indianmeal moth |
| Biology | Adults are nocturnal, sensitive to light and food odors, laying eggs on grain surfaces or packaging crevices. Larvae bore into grains, spin silk webs causing clumping and spoilage, while excreting frass that contaminates stored products. This species thrives in warehouses and kitchens, completing multiple generations annually (24–30 °C). |
| Damage | Primary hosts include wheat, maize, rice, legumes, oilseeds, dried fruits, and medicinal materials. |
| Distribution Regions | Global grain storage facilities. |
| Monitoring | Pheromone lures mimic natural sex pheromones to attract male insects into specialized traps for population monitoring and suppression. As a core IPM component, monitoring enables early risk detection and targeted control. Mass trapping reduces mating opportunities to curb offspring populations. Protocols: ●Use only with matched traps. ●15-45 traps/hectare,replace/replenish every 4-6 weeks. ●Wear gloves or wash hands with detergent when switching lure types. ●Refer to trap-specific hanging instructions. |
| Recommended Traps | Delta Trap, Wing Trap |

Teilen Sie Ihre Kontaktinformationen, um präzise passende Pheromonlösungen zu erhalten. Sollte unser bestehendes Portfolio keine optimale Lösung bieten, initiiert unser Synthesechemie-Team eine kundenspezifische Entwicklung – vom Molekülstrukturdesign bis zur skalierten Produktion.